Table of Contents:
- What Is Healthcare Compliance?
- Who Regulates Healthcare Compliance?
- Why Is Compliance Important in Healthcare?
- What Are the Three Areas of Healthcare Compliance?
- Consequences of Non-Compliance
- Technology’s Role in Healthcare Compliance
- Partner With Healthcare Compliance Experts
Healthcare is one of the most strictly regulated industries because professionals like doctors and nurses hold lives in their hands. Health providers must deliver essential care while adhering to stringent legal and ethical standards. Various government authorities and accreditation organizations govern healthcare compliance. This discipline involves practices like billing and handling sensitive patient information.
Our guide will explain what healthcare compliance entails, who regulates it, and the consequences of non-compliance.
What Is Healthcare Compliance?
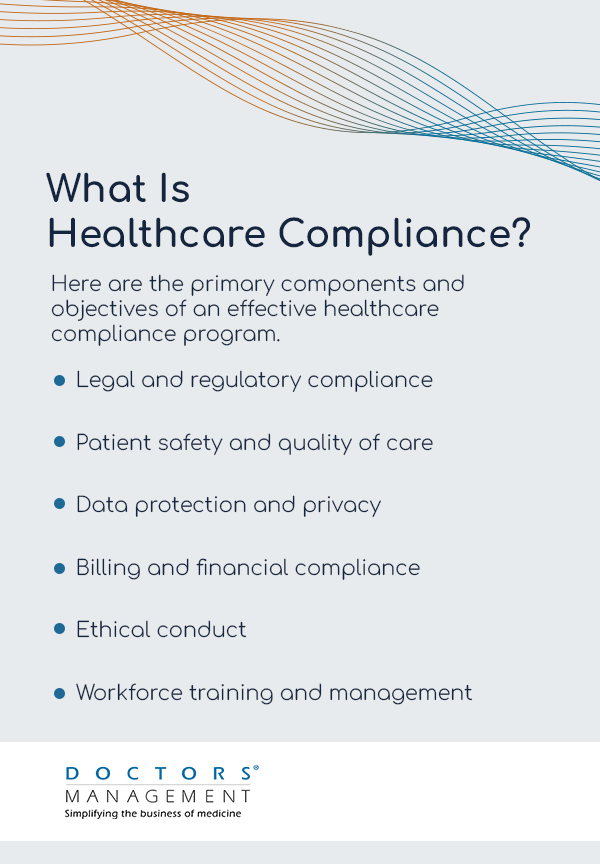
Healthcare compliance is a multifaceted and ongoing process that requires collaboration among providers, administrators, legal teams, and regulatory bodies. It involves developing policies and procedures, conducting training and education, implementing monitoring and auditing processes, and taking corrective actions to prevent non-compliance. Compliance programs include areas such as patient care, billing, data privacy, security, and fraud prevention. Their ultimate goal is to deliver safe, high-quality, and principled healthcare services.
Here are the primary components and objectives of an effective healthcare compliance program.
- Legal and regulatory compliance: Health providers must follow state, federal, and worldwide laws.
- Patient safety and quality of care: Compliance minimizes medical errors and enhances patient outcomes. It is all about ensuring care delivery with the latest evidence-based practices.
- Data protection and privacy: This area includes physical, administrative, and technical safeguards from unauthorized access and breaches.
- Billing and financial compliance: Standard billing and financial compliance ease reimbursement and reduce fraud. Additionally, ensuring compliance finance helps maintain accuracy in billing practices and financial integrity.
- Ethical conduct: Organizations should uphold all standards of care and operations. A committee may help guide decision-making and resolve moral dilemmas.
- Workforce training and management: Health employees commit to ongoing education. Training consists of the latest research in their respective fields, ethical and legal standards, and compliance workshops.
Healthcare compliance is a global effort. While each country has different laws, regulations, and governing entities, the core principle remains the same worldwide. The World Health Organization promotes the benefits of compliance programs and supports adherence to international regulations.
Who Regulates Healthcare Compliance?
Various federal, state, and local entities govern healthcare compliance. Your organization may also belong to professional boards or regulatory bodies with specific standards to uphold.
Government Acts
The government has passed several laws to regulate the healthcare industry.
- The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act: Congress passed this legislation in 1996 as a federal law restricting the release of private patient information. This law also ensures people can maintain health insurance coverage when they lose or change jobs. HIPAA reduces fraud in the healthcare system and gives patients with existing conditions better access to health insurance.
- The Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act: The HITECH Act, part of 2009’s American Recovery and Reinvestment Act, incentivized the meaningful use of electronic health records and strengthened HIPAA’s privacy and security provisions.
- The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act: ACA is a comprehensive health care reform law enacted in March 2010. This law allows people with existing health conditions or limited finances to obtain affordable health coverage through their state’s health insurance marketplace.
Federal Agencies
These federal agencies also regulate healthcare compliance.
- Department of Health and Human Services: The HHS is the cabinet-level federal government department that oversees health and welfare for all Americans. This agency is responsible for health insurance programs like Medicare, Medicaid, and the Children’s Health Insurance Program. Medicare is a federal program primarily covering people 65 and older, while CHIP and Medicaid provide coverage to everyone from children to older adults. These programs also provide coverage for people with disabilities and existing health conditions.
- The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services: CMS improves health outcomes by building on the ACA to expand access to quality, affordable insurance coverage. The organization sets reimbursement standards, coding, and billing compliance to prevent fraud and abuse. They insist on accurately documenting and coding services and regularly update these systems.
Accreditation Bodies
These accreditation bodies oversee medical practice compliance.
- The Joint Commission: The Joint Commission is a national organization focused on patient care quality, safety, and organizational management. Their resources, education, and training programs help providers improve their performance and compliance. Earning Joint Commission accreditation is a testament to an organization’s adherence to quality and safety goals.
- Commission on Accreditation of Rehabilitation Facilities: Unlike the other agencies listed in this guide, CARF is a nonprofit accreditor of health and human services. It is active in healthcare compliance, specifically in rehabilitation. It allows organizations to enhance their service quality and follow an international standard that is independent of local regulations.
Professional Boards and Associations
Since 1847, the American Medical Association has represented physicians’ interests at federal and state levels, engaging in healthcare policy developments and advocacy. They also publish the AMA Code of Medical Ethics, which sets the standards for the profession.
The AMA publishes research findings and journals, disseminating information throughout the industry. They provide various resources and tools to support physicians in their practice, including guidelines and health information technology. AMA membership is open to all physicians and medical students, giving opportunities for professional development, networking, and advocacy participation.
Why Is Compliance Important in Healthcare?
Compliance is important in healthcare because health providers must follow laws like HIPAA to avoid fines, lost licenses, and other penalties. There are also best practices for medical coding and billing and ethical guidelines concerning patient privacy. Ultimately, all these exist to protect patients from potential harm and ensure the delivery of quality care. Compliance helps healthcare organizations establish and maintain protocols, procedures, and guidelines that prioritize patient safety throughout all aspects of care delivery.

Complying with privacy and security regulations safeguards people’s private health information, prevents errors, and improves the patient experience. Health providers must implement appropriate measures to protect patient data from unauthorized access, breaches, and misuse. Compliance ensures the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of patient information, fostering trust between patients and physicians.
Principles such as respect for bodily autonomy encourage health professionals to provide care in their patient’s best interest. Organizations that uphold high standards maintain trust, professionalism, and integrity Compliance may also involve implementing evidence-based practices, monitoring patient outcomes, and continuously improving processes.
One way to instill the importance of compliance in your healthcare facility is to integrate it into the culture. The organization’s leadership must set the tone by modeling appropriate behavior. Other strategies to consider are conducting regular risk assessments, doing internal audits, and monitoring and identifying any compliance gaps before they become an issue.
How Compliance Programs Prevent Fraud
Healthcare regulations ensure financial integrity and transparency with accurate billing, coding, and documentation practices that prevent fraud, waste, and abuse. According to CMS data, national health expenditures grew to $4.5 trillion in 2022 — a 4.1% increase. Additionally, Medicare and Medicaid have proved to be tempting targets for fraudsters. Estimated annual fraud in the healthcare industry is at least $100 billion, but some experts suggest that figure should be even higher.
Compliance programs reduce fraud risks. Adhering to billing and code standards results in fewer errors and opportunities to cheat the system. Regular audits and checks will catch any issues early and allow organizations to solve problems before they escalate. Additionally, facilities can set up confidential hotlines where employees can anonymously report suspected fraud or compliance violations. Whistleblower protection measures help employees feel safe and protected when reporting potential fraud, encouraging early detection and prevention.
A robust compliance program should also extend beyond internal employees to include oversight of vendors, contractors, and other third parties. Through due diligence processes and contractual agreements, healthcare organizations ensure these external entities adhere to applicable laws and regulations, reducing the risk of fraud through external partnerships.
What Are the Three Areas of Healthcare Compliance?
The three primary areas of healthcare compliance organizations must focus on are safety, privacy, and billing.
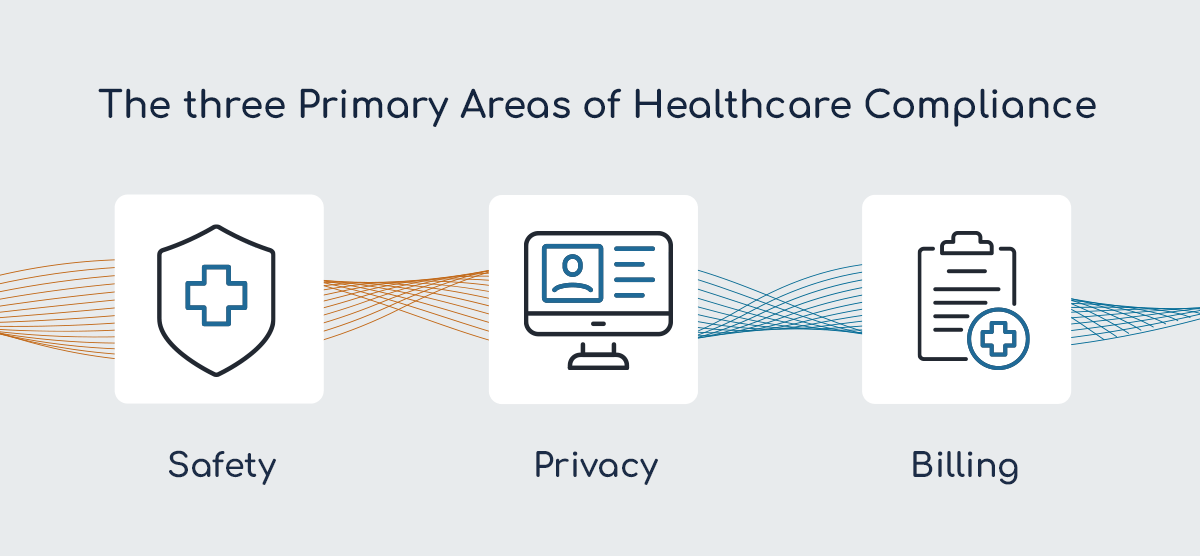
1. Safety
Healthcare delivery can be complex, making it challenging to adhere to consistent practices. The protocols healthcare providers and organizations implement to prevent harm must have these aspects.
- Error prevention: Fatigue and miscommunication can lead to human errors like dangerous drug interactions. Health providers must take measures to prevent mistakes and ensure surgical safety, like pre-operative checklists and post-operative care.
- Infection control: Infection control practices include hand-washing, hygiene, and instrument sterilization.
- Facility safety: All healthcare environments must be safe and conducive to patient care, especially the facility design.
- Patient identification: Accurate patient identification is critical in contexts like blood transfusions and medication administration.
2. Privacy
Health providers must keep patient information, prescriptions, and medical histories confidential and disclose them only in appropriate circumstances. These regulations primarily concern HIPAA, which has a regulatory framework specifically enforced by the Office for Civil Rights.
Strong data measures protect electronic health records and other forms of patient data from unauthorized access or breaches. Patients must understand their privacy rights, and health providers must obtain consent before using or sharing private health information.
- Trust in the healthcare system: Patients should feel safe and comfortable at medical appointments. They might not share valuable information if they believe it could be vulnerable, which could result in a missed diagnosis.
- Legal and ethical obligations: Privacy is a legal requirement and a moral imperative all professionals should respect.
- Preventing discrimination: Many health conditions bring stigma that patients might not want to disclose.
3. Billing
All billing must be error-free. For accuracy and fraud prevention, health providers must use the correct codes for all procedures and services. Health organizations should also implement routine auditing and monitoring.
- Medical coding: Services, procedures, equipment, and diagnoses all have standardized codes. The most common coding system is the International Classifications of Diseases. There is also the Current Procedural Terminology for procedures.
- Claims submission and processing: The next step is to submit claims to insurers with all the details of the services and the correct codes. The claims must be accurate and comply with policies.
- Patient billing: Remaining balances like copays, deductibles, or services not covered by insurance are the patient’s responsibility.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
Assorted laws and regulations stipulate the need for health professionals to be compliant. Failure to adhere to these laws will result in various ramifications.
- Fines and penalties: For example, severe and willful HIPAA violations can cost thousands of dollars and result in prison time.
- Criminal charges: Professionals can face criminal charges for fraud or gross negligence.
- Loss of license and accreditations: In some cases, non-compliance can lead to the loss of a professional’s license or a healthcare organization’s accreditation.
Outside these severe consequences, health providers will also deal with reputational damage and increased scrutiny from other regulatory bodies.
How Often Should Healthcare Organizations Assess Their Compliance Programs?
An annual review is a best practice to ensure:
- An assessment of policies and procedures
- Training effectiveness
- Compliance with legal and regulatory changes
- All expiration dates
- Billing practices
Quarterly self-audits can keep everything up to date and in good shape for the full review.
Technology’s Role in Healthcare Compliance
Technological advancements have streamlined and integrated systems, letting healthcare professionals seamlessly communicate and collaborate. Here are some areas where adopting technology has benefited the healthcare industry.
- Electronic health records: EHRs allow providers in different facilities to access consistent, accurate, and complete patient documentation. The system reduces the risk of errors and complies with HIPAA privacy regulations.
- Data security and privacy technologies: Cyber threats constantly challenge health professionals. While EHRs enable information sharing and transparency, which benefits patients and providers, they also elevate the risk of a third party accessing the information. Fortunately, data security has caught up over time, and today, technology can prevent unauthorized access.
- Artificial intelligence and analytics: AI tools can quickly analyze vast amounts of data to identify compliance risks. These systems can predict potential violations and offer recommendations for improvements. They can also flag anomalies and deviations from standards.
- Training and educational platforms: Providers must stay abreast of the latest information as the healthcare industry evolves. Online learning management systems, webinars, and e-learning modules disseminate up-to-date compliance information, policies, and procedures. Compliance platforms facilitate interactive learning through quizzes, simulations, and case studies, enhancing knowledge retention. Healthcare providers can easily access these resources, enhancing their knowledge and understanding of compliance requirements and other best practices without leaving their patients to travel to an in-person seminar.
Partner With Healthcare Compliance Experts
Compliance rules and regulations must meet an ever-changing world of needs and technologies. Healthcare organizations can create a culture of accountability, transparency, and excellence by prioritizing compliance and adhering to requirements governing data privacy and security, ethical standards, and financial integrity.
DoctorsManagement, LLC, offers experienced auditing services for healthcare compliance. We can create comprehensive, successful, and sustainable compliance systems for your practice. But it doesn’t end there. We also have consulting and training to help you implement the recommendations from our auditing assessment.
We will customize our compliance services to meet your unique needs and provide the best solutions for your organization. Schedule your free consultation today.